面试官:你了解vue的diff算法吗?说说看
一、是什么 diff 算法是一种通过同层的树节点进行比较的高效算法
其有两个特点:
比较只会在同层级进行, 不会跨层级比较
在diff比较的过程中,循环从两边向中间比较
diff 算法在很多场景下都有应用,在 vue 中,作用于虚拟 dom 渲染成真实 dom 的新旧 VNode 节点比较
二、比较方式 diff整体策略为:深度优先,同层比较
比较只会在同层级进行, 不会跨层级比较
比较的过程中,循环从两边向中间收拢
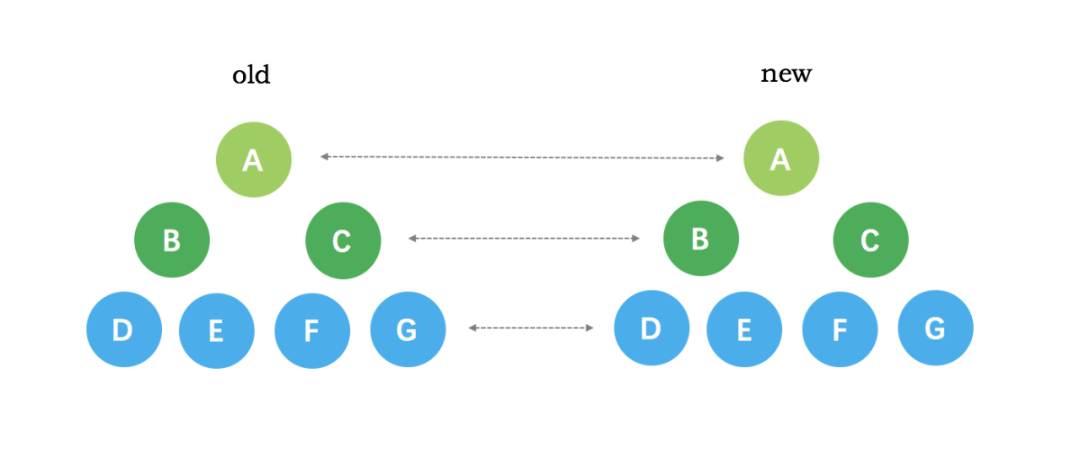
下面举个vue通过diff算法更新的例子:
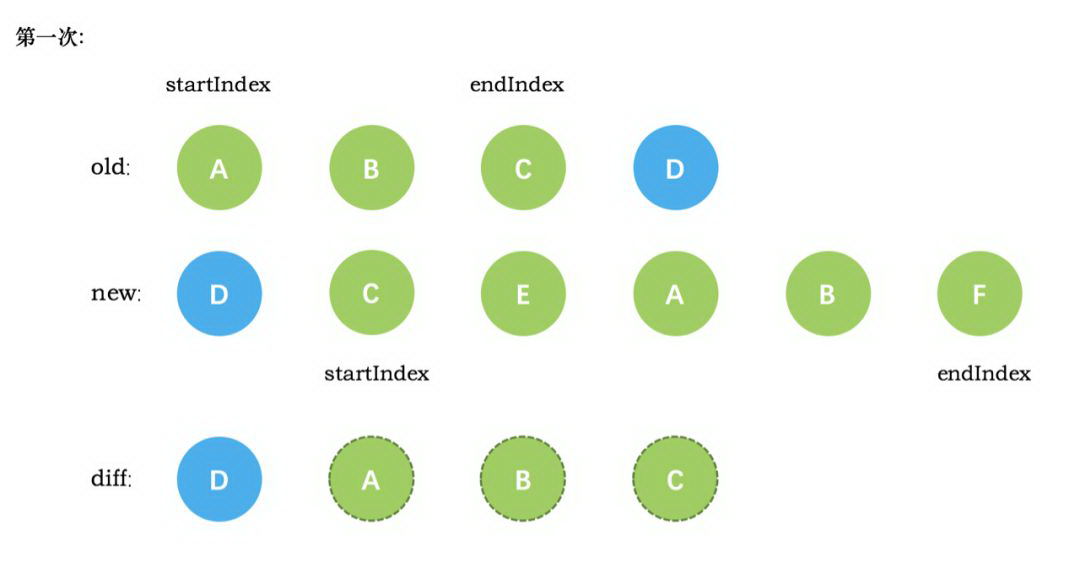
新旧VNode节点如下图所示:
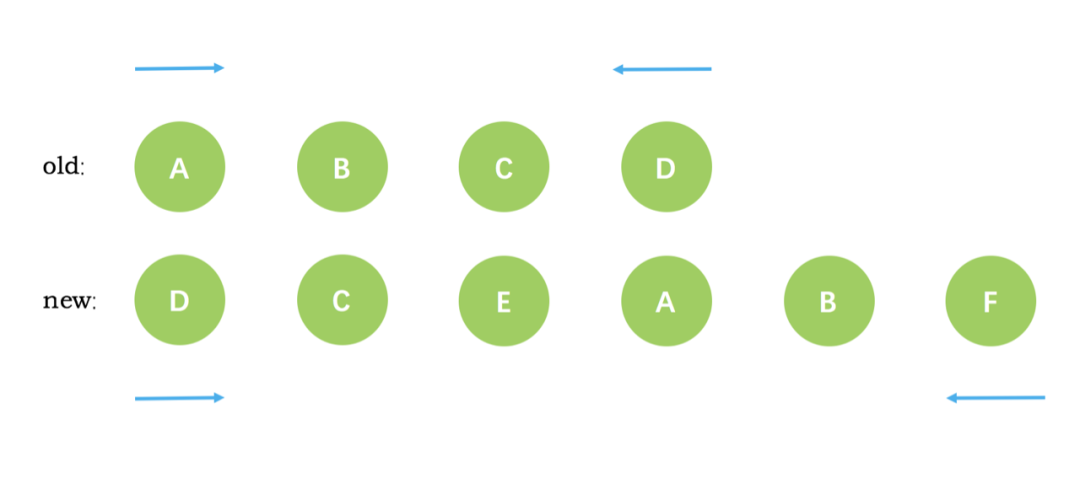
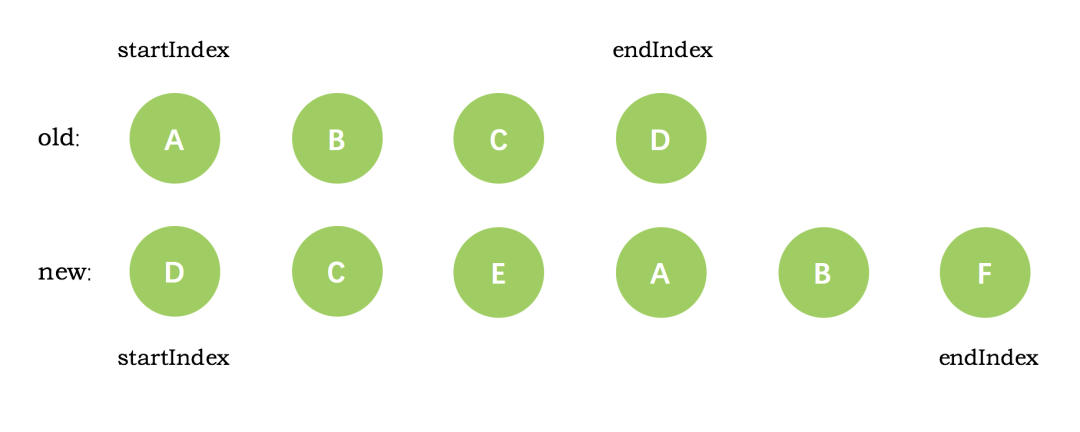
第一次循环后,发现旧节点D与新节点D相同,直接复用旧节点D作为diff后的第一个真实节点,同时旧节点endIndex移动到C,新节点的 startIndex 移动到了 C
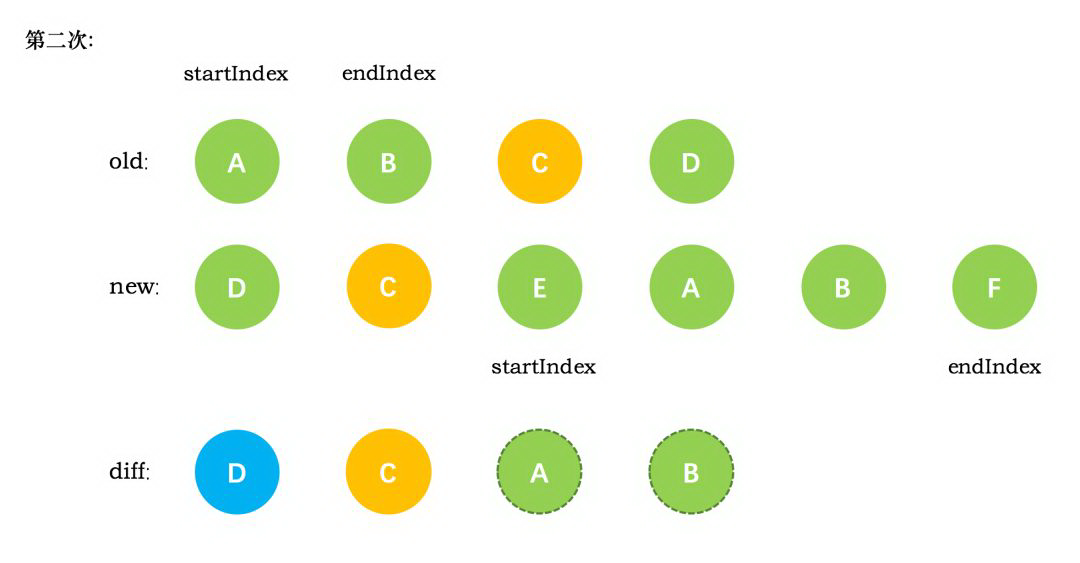
第二次循环后,同样是旧节点的末尾和新节点的开头(都是 C)相同,同理,diff 后创建了 C 的真实节点插入到第一次创建的 D 节点后面。同时旧节点的 endIndex 移动到了 B,新节点的 startIndex 移动到了 E
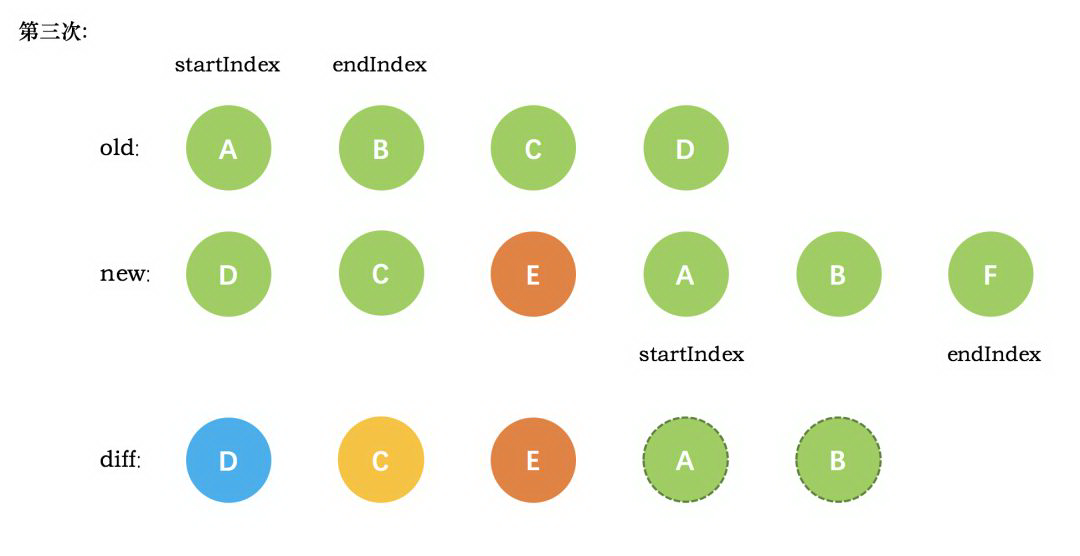
第三次循环中,发现E没有找到,这时候只能直接创建新的真实节点 E,插入到第二次创建的 C 节点之后。同时新节点的 startIndex 移动到了 A。旧节点的 startIndex 和 endIndex 都保持不动
第四次循环中,发现了新旧节点的开头(都是 A)相同,于是 diff 后创建了 A 的真实节点,插入到前一次创建的 E 节点后面。同时旧节点的 startIndex 移动到了 B,新节点的 startIndex 移动到了 B
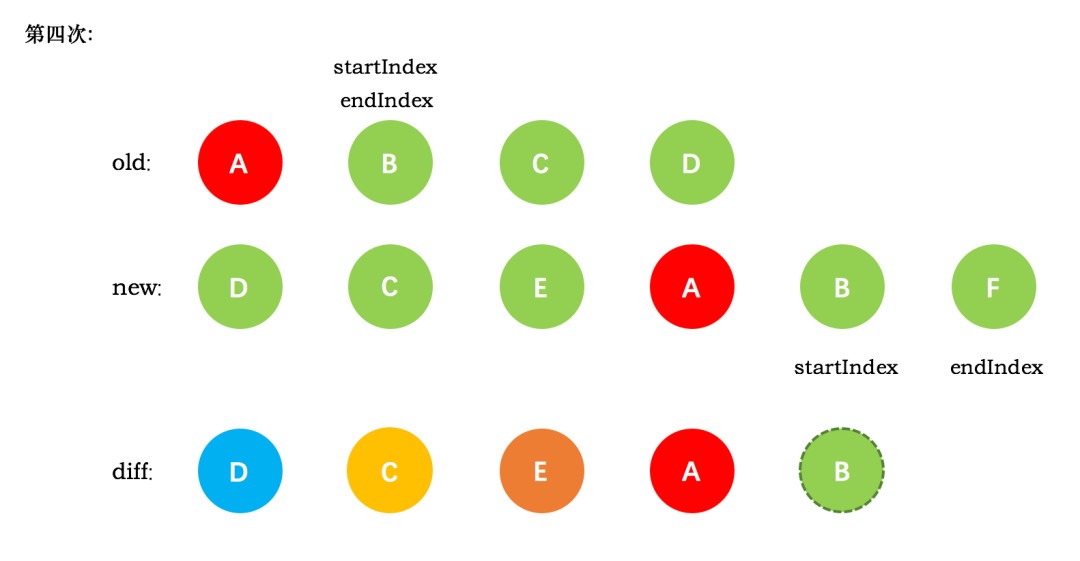
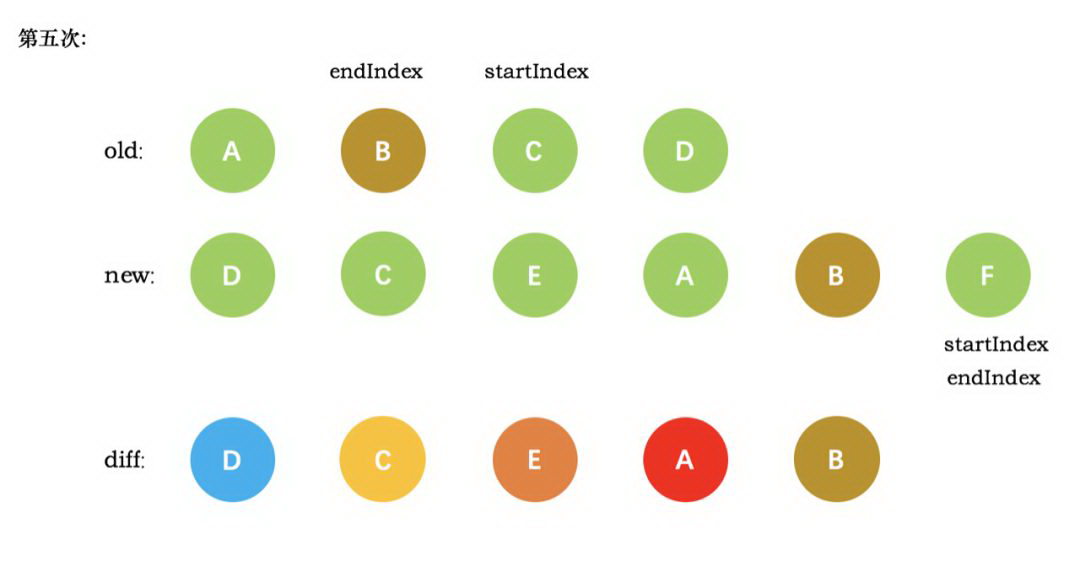
第五次循环中,情形同第四次循环一样,因此 diff 后创建了 B 真实节点 插入到前一次创建的 A 节点后面。同时旧节点的 startIndex 移动到了 C,新节点的 startIndex 移动到了 F
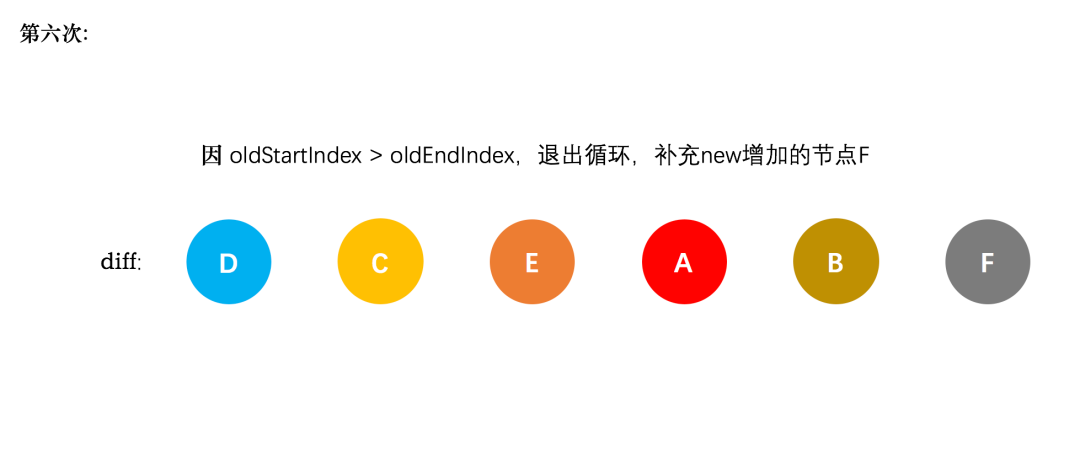
新节点的 startIndex 已经大于 endIndex 了,需要创建 newStartIdx 和 newEndIdx 之间的所有节点,也就是节点F,直接创建 F 节点对应的真实节点放到 B 节点后面
三、原理分析 当数据发生改变时,set方法会调用Dep.notify通知所有订阅者Watcher,订阅者就会调用patch给真实的DOM打补丁,更新相应的视图
源码位置:src/core/vdom/patch.js
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 function patch (oldVnode, vnode, hydrating, removeOnly ) { if (isUndef (vnode)) { if (isDef (oldVnode)) invokeDestroyHook (oldVnode) return } let isInitialPatch = false const insertedVnodeQueue = [] if (isUndef (oldVnode)) { isInitialPatch = true createElm (vnode, insertedVnodeQueue) } else { const isRealElement = isDef (oldVnode.nodeType ) if (!isRealElement && sameVnode (oldVnode, vnode)) { patchVnode (oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, null , null , removeOnly) } else { if (isRealElement) { if (oldVnode.nodeType === 1 && oldVnode.hasAttribute (SSR_ATTR )) { oldVnode.removeAttribute (SSR_ATTR ) hydrating = true } if (isTrue (hydrating)) { if (hydrate (oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue)) { invokeInsertHook (vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, true ) return oldVnode } } oldVnode = emptyNodeAt (oldVnode) } return vnode.elm } } }
patch函数前两个参数位为oldVnode 和 Vnode ,分别代表新的节点和之前的旧节点,主要做了四个判断:
没有新节点,直接触发旧节点的destory钩子
没有旧节点,说明是页面刚开始初始化的时候,此时,根本不需要比较了,直接全是新建,所以只调用 createElm
旧节点和新节点自身一样,通过 sameVnode 判断节点是否一样,一样时,直接调用 patchVnode 去处理这两个节点
旧节点和新节点自身不一样,当两个节点不一样的时候,直接创建新节点,删除旧节点
下面主要讲的是patchVnode部分
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 function patchVnode (oldVnode, vnode, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly) { if (oldVnode === vnode) { return } const elm = vnode.elm = oldVnode.elm if (isTrue (oldVnode.isAsyncPlaceholder )) { if (isDef (vnode.asyncFactory .resolved )) { hydrate (oldVnode.elm , vnode, insertedVnodeQueue) } else { vnode.isAsyncPlaceholder = true } return } if (isTrue (vnode.isStatic ) && isTrue (oldVnode.isStatic ) && vnode.key === oldVnode.key && (isTrue (vnode.isCloned ) || isTrue (vnode.isOnce )) ) { vnode.componentInstance = oldVnode.componentInstance return } let i const data = vnode.data if (isDef (data) && isDef (i = data.hook ) && isDef (i = i.prepatch )) { i (oldVnode, vnode) } const oldCh = oldVnode.children const ch = vnode.children if (isDef (data) && isPatchable (vnode)) { for (i = 0 ; i < cbs.update .length ; ++i) cbs.update [i](oldVnode, vnode) if (isDef (i = data.hook ) && isDef (i = i.update )) i (oldVnode, vnode) } if (isUndef (vnode.text )) { if (isDef (oldCh) && isDef (ch)) { if (oldCh !== ch) updateChildren (elm, oldCh, ch, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly) } else if (isDef (ch)) { if (isDef (oldVnode.text )) nodeOps.setTextContent (elm, '' ) addVnodes (elm, null , ch, 0 , ch.length - 1 , insertedVnodeQueue) } else if (isDef (oldCh)) { removeVnodes (elm, oldCh, 0 , oldCh.length - 1 ) } else if (isDef (oldVnode.text )) { nodeOps.setTextContent (elm, '' ) } } else if (oldVnode.text !== vnode.text ) { nodeOps.setTextContent (elm, vnode.text ) } if (isDef (data)) { if (isDef (i = data.hook ) && isDef (i = i.postpatch )) i (oldVnode, vnode) } }
patchVnode主要做了几个判断:
新节点是否是文本节点,如果是,则直接更新dom的文本内容为新节点的文本内容
新节点和旧节点如果都有子节点,则处理比较更新子节点
只有新节点有子节点,旧节点没有,那么不用比较了,所有节点都是全新的,所以直接全部新建就好了,新建是指创建出所有新DOM,并且添加进父节点
只有旧节点有子节点而新节点没有,说明更新后的页面,旧节点全部都不见了,那么要做的,就是把所有的旧节点删除,也就是直接把DOM 删除
子节点不完全一致,则调用updateChildren
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 function updateChildren (parentElm, oldCh, newCh, insertedVnodeQueue, removeOnly) { let oldStartIdx = 0 let newStartIdx = 0 let oldEndIdx = oldCh.length - 1 let newEndIdx = newCh.length - 1 let oldStartVnode = oldCh[0 ] let oldEndVnode = oldCh[oldEndIdx] let newStartVnode = newCh[0 ] let newEndVnode = newCh[newEndIdx] let oldKeyToIdx, idxInOld, vnodeToMove, refElm const canMove = !removeOnly while (oldStartIdx <= oldEndIdx && newStartIdx <= newEndIdx) { if (isUndef (oldStartVnode)) { oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx] } else if (isUndef (oldEndVnode)) { oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx] } else if (sameVnode (oldStartVnode, newStartVnode)) { patchVnode (oldStartVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue) oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx] newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx] } else if (sameVnode (oldEndVnode, newEndVnode)) { patchVnode (oldEndVnode, newEndVnode, insertedVnodeQueue) oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx] newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx] } else if (sameVnode (oldStartVnode, newEndVnode)) { patchVnode (oldStartVnode, newEndVnode, insertedVnodeQueue) canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore (parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm , nodeOps.nextSibling (oldEndVnode.elm )) oldStartVnode = oldCh[++oldStartIdx] newEndVnode = newCh[--newEndIdx] } else if (sameVnode (oldEndVnode, newStartVnode)) { patchVnode (oldEndVnode, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue) canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore (parentElm, oldEndVnode.elm , oldStartVnode.elm ) oldEndVnode = oldCh[--oldEndIdx] newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx] } else { if (isUndef (oldKeyToIdx)) oldKeyToIdx = createKeyToOldIdx (oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx) idxInOld = isDef (newStartVnode.key ) ? oldKeyToIdx[newStartVnode.key ] : findIdxInOld (newStartVnode, oldCh, oldStartIdx, oldEndIdx) if (isUndef (idxInOld)) { createElm (newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm ) } else { vnodeToMove = oldCh[idxInOld] if (process.env .NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !vnodeToMove) { warn ( 'It seems there are duplicate keys that is causing an update error. ' + 'Make sure each v-for item has a unique key.' ) } if (sameVnode (vnodeToMove, newStartVnode)) { patchVnode (vnodeToMove, newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue) oldCh[idxInOld] = undefined canMove && nodeOps.insertBefore (parentElm, vnodeToMove.elm , oldStartVnode.elm ) } else { createElm (newStartVnode, insertedVnodeQueue, parentElm, oldStartVnode.elm ) } } newStartVnode = newCh[++newStartIdx] } }
while循环主要处理了以下五种情景:
当新老 VNode 节点的 start 相同时,直接 patchVnode ,同时新老 VNode 节点的开始索引都加 1
当新老 VNode 节点的 end相同时,同样直接 patchVnode ,同时新老 VNode 节点的结束索引都减 1
当老 VNode 节点的 start 和新 VNode 节点的 end 相同时,这时候在 patchVnode 后,还需要将当前真实 dom 节点移动到 oldEndVnode 的后面,同时老 VNode 节点开始索引加 1,新 VNode 节点的结束索引减 1
当老 VNode 节点的 end 和新 VNode 节点的 start 相同时,这时候在 patchVnode 后,还需要将当前真实 dom 节点移动到 oldStartVnode 的前面,同时老 VNode 节点结束索引减 1,新 VNode 节点的开始索引加 1
如果都不满足以上四种情形,那说明没有相同的节点可以复用,则会分为以下两种情况:
从旧的 VNode 为 key 值,对应 index 序列为 value 值的哈希表中找到与 newStartVnode 一致 key 的旧的 VNode 节点,再进行patchVnode ,同时将这个真实 dom 移动到 oldStartVnode 对应的真实 dom 的前面
调用 createElm 创建一个新的 dom 节点放到当前 newStartIdx 的位置
小结
当数据发生改变时,订阅者watcher就会调用patch给真实的DOM打补丁
通过isSameVnode进行判断,相同则调用patchVnode方法
patchVnode做了以下操作:
找到对应的真实dom,称为el
如果都有都有文本节点且不相等,将el文本节点设置为Vnode的文本节点
如果oldVnode有子节点而VNode没有,则删除el子节点
如果oldVnode没有子节点而VNode有,则将VNode的子节点真实化后添加到el
如果两者都有子节点,则执行updateChildren函数比较子节点
updateChildren主要做了以下操作:
设置新旧VNode的头尾指针
新旧头尾指针进行比较,循环向中间靠拢,根据情况调用patchVnode进行patch重复流程、调用createElem创建一个新节点,从哈希表寻找 key一致的VNode 节点再分情况操作
参考文献